Car insurance coverage is a crucial aspect of responsible vehicle ownership, offering financial protection against unforeseen events. Understanding the various types of coverage, factors influencing premiums, and the claims process is essential for making informed decisions and ensuring adequate protection. This guide delves into the complexities of car insurance, empowering you to navigate this critical area with confidence and clarity.
From liability and collision coverage to the nuances of uninsured/underinsured motorist protection, we’ll explore the key components of a comprehensive car insurance policy. We’ll also examine how factors like driving history, age, location, and credit score impact premiums, and provide strategies for securing the best possible rates. Finally, we’ll guide you through the process of filing a claim and understanding your policy documents.
Types of Car Insurance Coverage
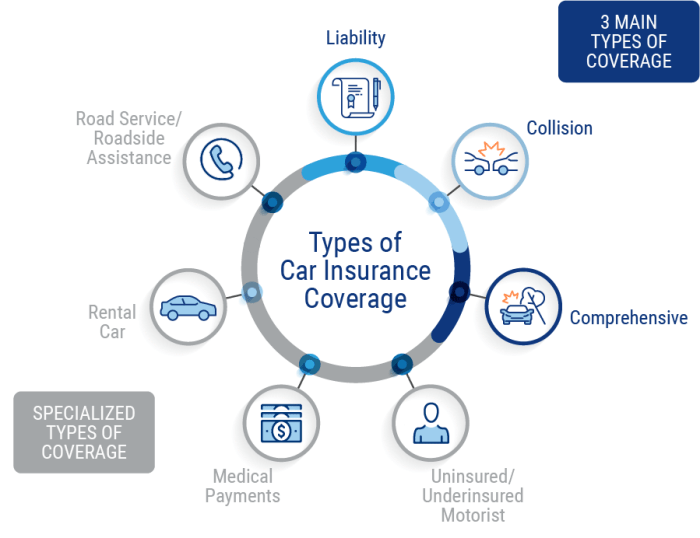
Choosing the right car insurance can feel overwhelming, but understanding the different types of coverage available is the first step to securing adequate protection. This section will detail the key types of car insurance coverage, helping you make informed decisions about your policy.
Liability Coverage, Car insurance coverage
Liability coverage protects you financially if you cause an accident that injures someone or damages their property. It’s typically broken down into two parts: bodily injury liability and property damage liability. Bodily injury liability covers medical expenses, lost wages, and pain and suffering for those injured in an accident you caused. Property damage liability covers the cost of repairing or replacing the other person’s vehicle or property. The limits of your liability coverage are expressed as numbers, such as 100/300/100. This means $100,000 per person for bodily injury, $300,000 total for all bodily injuries in an accident, and $100,000 for property damage. It’s crucial to choose limits that reflect your potential liability. Higher limits offer greater protection but usually come with a higher premium.
Collision Coverage
Collision coverage pays for damage to your vehicle, regardless of who is at fault, if the damage results from a collision with another vehicle or object, such as a tree or a fence. This coverage is beneficial because it protects you even if you are at fault for the accident. For example, if you rear-end another car, collision coverage will help pay for the repairs to your vehicle, even if you are deemed responsible for the accident. The deductible you choose will affect how much you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance kicks in.
Comprehensive Coverage
Comprehensive coverage protects your vehicle from damage caused by events other than collisions. This includes things like theft, vandalism, fire, hail, flood, and even damage from animals. For instance, if a tree falls on your car during a storm, comprehensive coverage would help cover the repair costs. However, comprehensive coverage typically excludes damage caused by wear and tear or mechanical failure. Like collision coverage, it usually has a deductible.
Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage
Uninsured/underinsured motorist (UM/UIM) coverage protects you if you’re involved in an accident with a driver who is uninsured or whose insurance coverage is insufficient to cover your injuries or damages. This is a critical coverage because it can protect you from significant financial losses if the at-fault driver lacks adequate insurance. For example, if you are seriously injured by an uninsured driver, your UM/UIM coverage can help pay for your medical bills and lost wages. This coverage is separate from liability coverage and is crucial to consider, especially in areas with a high percentage of uninsured drivers.
| Coverage Type | Description | What it Covers | Exclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liability | Protects you if you cause an accident that injures someone or damages their property. | Medical expenses, lost wages, pain and suffering of others; repair or replacement of others’ property. | Damage to your own vehicle; injuries to you or your passengers. |
| Collision | Covers damage to your vehicle resulting from a collision with another vehicle or object. | Repairs or replacement of your vehicle after a collision, regardless of fault. | Damage from events not involving a collision (e.g., fire, theft); damage due to wear and tear. |
| Comprehensive | Covers damage to your vehicle from events other than collisions. | Damage from fire, theft, vandalism, hail, flood, and other non-collision events. | Damage from collisions; damage due to wear and tear or mechanical failure. |
| Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist | Protects you if you’re involved in an accident with an uninsured or underinsured driver. | Medical expenses, lost wages, pain and suffering for you and your passengers resulting from an accident with an uninsured or underinsured driver. | Damage to your own vehicle if the other driver is at fault but uninsured/underinsured (unless you have collision coverage). |
Factors Affecting Car Insurance Premiums
Several interconnected factors influence the cost of your car insurance premiums. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions and potentially save money. Insurance companies use a complex algorithm to assess risk, and the elements described below are key components of that calculation.
Driving History’s Impact on Premiums
Your driving record significantly impacts your insurance rates. Accidents and traffic violations are major factors. A single at-fault accident can lead to a substantial premium increase, often lasting several years. Similarly, multiple speeding tickets or other moving violations demonstrate a higher risk profile, resulting in higher premiums. Conversely, maintaining a clean driving record with no accidents or tickets for an extended period often leads to lower premiums and potentially discounts from your insurer. For example, a driver with three accidents in the past five years will likely pay significantly more than a driver with a spotless record.
Age, Gender, and Location Influences
Insurance companies statistically analyze data to determine risk based on age, gender, and location. Younger drivers, particularly those under 25, typically pay higher premiums due to statistically higher accident rates in this demographic. Gender can also play a role, although this is becoming less significant in many regions due to regulatory changes promoting gender neutrality in insurance pricing. Location is a crucial factor because accident rates, theft rates, and repair costs vary widely by geographic area. Living in a high-crime area or an area with frequent accidents will generally result in higher premiums.
Credit Score’s Role in Determining Rates
In many regions, your credit score plays a role in determining your car insurance premium. Insurers often view a lower credit score as an indicator of higher risk. The reasoning behind this is that individuals with poor credit management may be more likely to take risks in other areas of their lives, including driving. This correlation, however, is controversial, with some arguing that it unfairly penalizes individuals with low credit scores who may be otherwise safe drivers. However, it remains a significant factor in many insurance companies’ rating systems. A higher credit score can often translate to lower premiums.
Strategies for Lowering Car Insurance Premiums
Several strategies can help lower your car insurance premiums. Understanding these options and implementing them can lead to significant savings.
- Maintain a clean driving record: Avoiding accidents and traffic violations is the most effective way to keep premiums low.
- Improve your credit score: Working to improve your credit score can lead to lower insurance rates in regions where credit is a rating factor.
- Choose a higher deductible: Opting for a higher deductible means you’ll pay more out-of-pocket in the event of a claim, but your premiums will be lower.
- Bundle your insurance policies: Many insurers offer discounts for bundling car insurance with other types of insurance, such as homeowners or renters insurance.
- Shop around and compare rates: Getting quotes from multiple insurers ensures you find the best rates for your needs.
- Consider safety features: Cars equipped with advanced safety features, such as anti-lock brakes and airbags, may qualify for discounts.
- Maintain a good driving history: This includes avoiding speeding tickets, reckless driving citations, and accidents.
- Take a defensive driving course: Completing a defensive driving course may qualify you for a discount, demonstrating your commitment to safe driving practices.
Choosing the Right Coverage
Selecting the right car insurance coverage involves a careful assessment of your individual needs and risk tolerance. The goal is to find a balance between adequate protection and affordable premiums. This requires understanding the different coverage options and how they apply to your specific circumstances.
Determining Liability Coverage
Liability coverage protects you financially if you cause an accident that injures someone or damages their property. The appropriate level depends on several factors, including your assets and the potential severity of accidents in your area. Higher liability limits offer greater protection but come with higher premiums. Consider your net worth and the potential cost of significant injuries or property damage. For example, a minimum liability limit might suffice for someone with few assets, while someone with substantial wealth might opt for much higher limits to safeguard their assets. A thorough evaluation of personal risk is crucial in making this determination.
Collision and Comprehensive Coverage
Collision coverage pays for repairs to your vehicle if it’s damaged in an accident, regardless of fault. Comprehensive coverage protects against damage caused by events other than collisions, such as theft, vandalism, or weather-related incidents. Whether these are necessary depends on the age and value of your vehicle and your financial situation. For newer or more expensive cars, collision and comprehensive coverage can be beneficial to protect your investment. For older vehicles, the cost of these coverages might outweigh the potential benefits. A cost-benefit analysis considering the vehicle’s value and repair costs versus premium increases is essential.
Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage
Uninsured/underinsured motorist (UM/UIM) coverage protects you if you’re injured by an uninsured or underinsured driver. It’s crucial because many drivers operate without adequate insurance. UM/UIM coverage compensates you for medical expenses, lost wages, and other damages. The level of UM/UIM coverage should be sufficient to cover potential losses in the event of a serious accident. Consider the possibility of facing significant medical bills and lost income without sufficient insurance from the at-fault party; choosing a higher limit offers greater financial security in such a situation.
Deductible Options
Deductibles represent the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Higher deductibles generally result in lower premiums, while lower deductibles mean higher premiums. Choosing a deductible involves balancing affordability with out-of-pocket expense in the event of a claim. For example, a higher deductible ($1000) will lead to lower monthly premiums, but you’ll pay more if you need to file a claim. Conversely, a lower deductible ($250) will increase your monthly payments, but you’ll pay less out-of-pocket in case of a claim. The decision hinges on your risk tolerance and financial capabilities.
Decision-Making Flowchart for Car Insurance Coverage
A flowchart would visually represent the decision-making process. It would start with assessing your assets and risk tolerance, branching to questions about your vehicle’s age and value, leading to decisions on liability, collision, comprehensive, and UM/UIM coverage levels. Finally, it would conclude with the selection of a deductible based on the preferred balance between premium cost and out-of-pocket expenses. The flowchart’s structure would mirror the logical steps in determining the appropriate level of car insurance coverage. The final decision would reflect a personalized balance of risk mitigation and affordability.
Understanding Policy Documents and Clauses
Your car insurance policy is a legally binding contract outlining your coverage and responsibilities. Understanding its contents is crucial to ensuring you receive the appropriate protection in case of an accident or other covered event. A thorough understanding of the policy’s clauses and exclusions will prevent unexpected costs and disputes with your insurance provider.
Common Components of a Standard Car Insurance Policy
A typical car insurance policy includes several key sections. These sections provide a comprehensive overview of the agreement between you and the insurance company, detailing your coverage, premiums, and responsibilities. Understanding each section is essential for making informed decisions regarding your insurance needs.
Key Policy Clauses and Their Implications
Policy clauses define the specific terms and conditions of your coverage. Some clauses might specify deductibles, outlining the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Others may describe the process for filing a claim, the types of damages covered, and the limitations on coverage amounts. Understanding these clauses is critical for navigating the claims process effectively and avoiding misunderstandings. For instance, a clause might limit liability coverage to a specific monetary amount, meaning you would be personally responsible for any damages exceeding that limit.
Reading and Understanding a Car Insurance Policy: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. Review the Declaration Page: This page summarizes your policy’s key information, including your coverage details, premium amounts, and policy period.
2. Examine the Coverage Sections: Carefully review each coverage section (e.g., liability, collision, comprehensive) to understand the extent of your protection. Pay close attention to any limitations or exclusions.
3. Understand Exclusions and Limitations: Identify what is not covered under your policy. This often includes specific events, types of damage, or situations.
4. Clarify Unclear Terms: If any terms or conditions are unclear, contact your insurance provider for clarification.
5. Keep a Copy of Your Policy: Maintain a readily accessible copy of your policy for future reference.
Examples of Common Exclusions and Limitations
Many policies exclude coverage for damages caused by intentional acts, driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs, or using the vehicle for unauthorized purposes (e.g., racing). Limitations might include a cap on the amount paid for repairs or a specific time limit for filing a claim. For example, wear and tear is typically excluded from comprehensive coverage, meaning damage due to normal aging of the vehicle won’t be covered. Similarly, damage caused by driving a vehicle without a valid driver’s license is frequently excluded.
Sample Car Insurance Policy: Key Sections
Declaration Page: This page details the policyholder’s information, coverage details, policy period, and premium. It acts as a summary of the entire agreement.
Liability Coverage: This section Artikels the insurance company’s responsibility to pay for damages caused to others in an accident you are at fault for. It includes bodily injury and property damage liability.
Collision Coverage: This covers damages to your vehicle resulting from a collision with another vehicle or object, regardless of fault.
Comprehensive Coverage: This protects your vehicle against damages not related to collisions, such as theft, vandalism, fire, or weather-related damage.
Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: This provides protection if you are involved in an accident caused by an uninsured or underinsured driver.
Medical Payments Coverage: This pays for medical expenses for you and your passengers, regardless of fault.
Exclusions and Limitations: This section specifies events, circumstances, or damages that are not covered under the policy.
Filing a Claim
Filing a car insurance claim can seem daunting, but understanding the process can make it significantly smoother. This section Artikels the steps involved, the necessary information, effective communication strategies, and a typical timeline. Remember, prompt and accurate reporting is crucial for a successful claim.
Steps Involved in Filing a Car Insurance Claim
The claims process generally begins with immediate notification to your insurance provider. This is usually followed by a detailed account of the incident, including the date, time, location, and circumstances. Next, you’ll need to provide supporting documentation. Your insurer will then investigate the claim, potentially contacting witnesses or reviewing police reports. Following the investigation, a determination will be made regarding liability and the extent of coverage. Finally, once approved, the claim will be processed, and compensation will be disbursed.
Information Required to File a Claim Effectively
Accurate and comprehensive information is essential for a swift claim resolution. This includes details about the accident itself—date, time, location, and a description of the events. Crucially, you’ll need the contact and insurance information of all parties involved, including witnesses. Information about your vehicle—make, model, year, VIN—is also necessary, as is photographic evidence of the damage sustained. Finally, details about any injuries sustained by you or others involved should be included. Providing all this information upfront streamlines the process and minimizes delays.
Communicating with the Insurance Company During the Claims Process
Clear and concise communication is key throughout the claims process. Respond promptly to all inquiries from your insurer and provide all requested information without delay. Maintain a professional and courteous demeanor, even if you feel frustrated. If you disagree with any aspect of the claim handling, express your concerns calmly and respectfully, citing relevant policy clauses or supporting evidence. Keep detailed records of all communication, including dates, times, and summaries of conversations. This documentation can be invaluable if disputes arise.
Typical Timeline for Processing a Car Insurance Claim
The timeline for processing a car insurance claim varies significantly depending on the complexity of the claim and the insurance company’s procedures. Simple claims, involving minor damage and clear liability, may be resolved within a few weeks. More complex claims, involving significant damage, multiple parties, or disputes over liability, can take several months or even longer to resolve. Factors like the availability of necessary documentation and the promptness of responses from all involved parties significantly impact the overall processing time. For example, a minor fender bender with readily available evidence might be resolved within 2-4 weeks, while a major accident involving injuries and legal proceedings could extend beyond several months.
Documentation Needed When Filing a Car Insurance Claim
Providing the correct documentation from the outset is crucial for a smooth claims process. Here’s a list of essential documents:
- Police report (if applicable)
- Photos and videos of the accident scene and vehicle damage
- Contact information of all parties involved, including witnesses
- Your insurance policy information
- Medical records and bills (if applicable)
- Repair estimates from certified mechanics
- Rental car receipts (if applicable)
Car Insurance and Different Life Stages: Car Insurance Coverage

Your car insurance needs evolve significantly throughout your life, influenced by factors like driving experience, family responsibilities, and the type of vehicle you own. Understanding these changes is crucial for securing adequate coverage at the right price. This section examines how car insurance requirements adapt to different life stages and vehicle types.
Young Drivers’ Insurance Needs
Young drivers, typically those under 25, are statistically more likely to be involved in accidents. Insurance companies reflect this higher risk with increased premiums. Young drivers often benefit from taking defensive driving courses to potentially lower their rates. Maintaining a clean driving record is paramount, as any accidents or traffic violations will significantly impact premiums. Consider opting for higher liability coverage to protect yourself financially in case of an accident. Exploring options like telematics programs, which track driving behavior, can also help demonstrate safe driving habits and potentially lead to lower premiums.
Family Drivers’ Insurance Considerations
Adding family members to your policy, particularly young drivers, will usually increase your premiums. However, bundling multiple vehicles or family members onto a single policy can often result in discounts. Comprehensive and collision coverage become increasingly important when protecting your family and their assets. Sufficient liability coverage is essential to cover potential damages caused to others in an accident. Consider adding uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage, which protects you if you’re involved in an accident with a driver lacking sufficient insurance.
Senior Citizens’ Changing Insurance Needs
As drivers age, their insurance needs may change. While senior citizens generally have more driving experience, their reaction times and vision might diminish, potentially leading to a higher risk profile. Some insurers offer discounts for senior drivers who complete defensive driving courses or participate in senior-focused driving programs. Reviewing coverage levels and adjusting them to reflect changes in driving habits or vehicle usage is important. Consider exploring options like reducing coverage amounts on older vehicles if their value has decreased significantly.
Insurance Options for Different Vehicle Types
Car insurance rates vary significantly depending on the type of vehicle. Cars generally have lower premiums compared to trucks, SUVs, and motorcycles. Trucks and SUVs, often larger and more powerful, typically carry higher premiums due to increased repair costs and a higher risk of causing significant damage in an accident. Motorcycles, due to their inherent vulnerability, usually have the highest insurance rates, reflecting the greater risk of injury and property damage. The type of coverage needed also varies; for example, comprehensive coverage might be less crucial for an older vehicle but essential for a newer, more expensive one, regardless of vehicle type.
| Life Stage | Vehicle Type | Recommended Coverage | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Young Driver | Car | Liability, Collision, Comprehensive | High premiums, defensive driving courses, telematics programs |
| Family Driver | SUV | Liability, Collision, Comprehensive, Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist | Bundling discounts, higher liability limits |
| Senior Citizen | Car | Liability, Collision (depending on vehicle age and value) | Discounts for defensive driving courses, potential coverage adjustments |
| Motorcycle Enthusiast | Motorcycle | Liability, Collision, Comprehensive, Medical Payments | High premiums, specialized coverage options |
Securing the right car insurance coverage is a vital step in responsible vehicle ownership. By understanding the different types of coverage available, the factors influencing premiums, and the claims process, you can make informed decisions that protect both your financial well-being and your peace of mind. Remember to regularly review your policy and adjust your coverage as your needs and circumstances change. Driving safely and maintaining a clean driving record are also key factors in keeping your premiums affordable.
Helpful Answers
What is the difference between a deductible and a premium?
A premium is the regular payment you make to your insurance company to maintain your coverage. A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in after an accident or incident.
Can I get car insurance if I have a poor driving record?
Yes, but you’ll likely pay higher premiums. Insurance companies consider your driving history when assessing risk. However, some companies specialize in high-risk drivers.
How often should I review my car insurance policy?
It’s advisable to review your car insurance policy at least annually, or whenever there’s a significant life change (e.g., new car, marriage, change of address).
What happens if I’m involved in an accident and the other driver is uninsured?
Uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage protects you in such situations. This coverage will help pay for your medical bills and vehicle repairs, even if the other driver is at fault and lacks insurance.
Can I bundle my car insurance with other types of insurance?
Yes, many insurance companies offer discounts for bundling car insurance with other types of insurance, such as homeowners or renters insurance. This can often lead to lower overall premiums.
